Introduction
When one thinks of India, the immediate image is often that of a diverse and vast nation, bursting at the seams with cultural, economic, and geographical variations. Two states that exemplify this diversity are Kerala and Uttar Pradesh (UP). While Kerala, in the southern tip of India, is known for its literacy rates, healthcare, and natural beauty, Uttar Pradesh, located in the northern heartland, is renowned for its historical significance, population size, and agricultural output. Comparing these two states i.e. Kerala vs Uttar Pradesh offers insights not just into their unique attributes but also into the larger fabric of India itself.
This article aims to provide an in-depth comparison of Kerala vs Uttar Pradesh, covering aspects ranging from geography and demographics to culture, economy, and infrastructure. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or just someone interested in understanding regional differences within India, this comprehensive guide will help you grasp the contrasts and commonalities between these two remarkable states.
Geographical Differences
Location and Topography
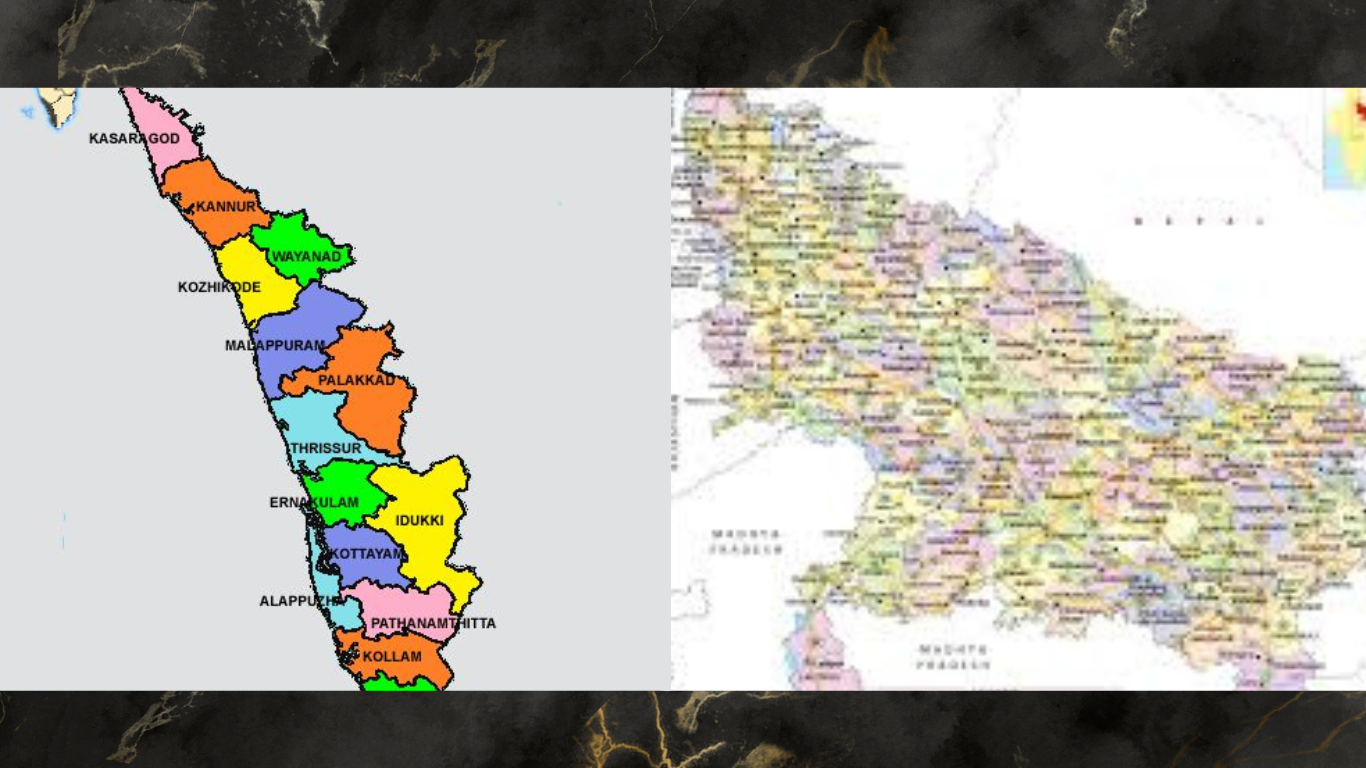
Kerala is located in the southwestern region of India, bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west and the Western Ghats to the east. The state’s landscape is characterized by its lush greenery, backwaters, and extensive coastline. The Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, play a significant role in shaping Kerala’s topography, making it rich in biodiversity and natural beauty.
In contrast, Uttar Pradesh lies in the northern part of India, sharing borders with Nepal to the north and several Indian states including Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan. The state is primarily part of the Indo-Gangetic plain, with fertile land fed by rivers like the Ganges, Yamuna, and their tributaries. The terrain is mostly flat, except for the Vindhya Range in the southern part of the state.
Climate Variations
Kerala enjoys a tropical climate, with significant rainfall during the monsoon season, which lasts from June to September. The state’s proximity to the equator means it experiences little variation in temperature throughout the year, with warm and humid conditions being the norm.
Uttar Pradesh, on the other hand, experiences a more varied climate. The state has hot summers, with temperatures often soaring above 40°C, a monsoon season from June to September, and cold winters, particularly in the northern parts where temperatures can drop to near freezing. The diverse climate conditions in UP influence its agriculture and living conditions significantly.
Natural Resources
Kerala’s natural resources include its rich biodiversity, forest products, spices, and marine resources. The Western Ghats are home to a wide variety of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to the region. Kerala is also famous for its spice plantations, including black pepper, cardamom, and clove.
Uttar Pradesh is endowed with fertile agricultural land, making it one of the largest producers of wheat, sugarcane, and rice in India. The state’s rivers are vital for irrigation, and its soil is rich in minerals, contributing to its agricultural productivity.
Demographic Comparison
Population Size and Density
Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state in India, with a population exceeding 230 million people. This makes it larger than many countries in terms of population. The state also has a high population density, particularly in urban areas like Lucknow, Kanpur, and Varanasi.
Kerala, in comparison, has a much smaller population of around 35 million. However, it has a high population density as well, particularly in cities like Thiruvananthapuram, Kochi, and Kozhikode. The state is known for its balanced rural and urban distribution, with many people living in semi-urban areas.
Urban vs Rural Distribution
Uttar Pradesh is predominantly rural, with about 77% of its population living in villages. Despite recent urbanization, the majority of the state’s population relies on agriculture and related activities for their livelihood. Urban centers like Lucknow and Noida are growing, but the state remains largely rural.
Kerala, on the other hand, has a unique settlement pattern where there is no clear distinction between urban and rural areas. The state is often described as having a “rurban” character, with urban amenities available even in rural areas. Approximately 52% of the population lives in urban or semi-urban areas, reflecting a more balanced distribution.
Literacy Rates and Educational Attainment
Kerala boasts the highest literacy rate in India, at around 96%. The state has made significant strides in education, with a strong emphasis on primary and secondary education. Higher education institutions in Kerala are also well-regarded, contributing to the state’s high Human Development Index (HDI).
Uttar Pradesh, while improving, still lags behind Kerala in literacy and educational attainment. The literacy rate in UP is about 70%, which is below the national average. The state faces challenges like high dropout rates, gender disparities in education, and inadequate infrastructure in schools, particularly in rural areas.
Cultural and Historical Background
Historical Significance of Kerala
Kerala has a rich history that dates back to ancient times. The state was a major center for the spice trade, attracting merchants from the Middle East, Europe, and Asia. The region was ruled by various dynasties, including the Cheras, Cholas, and Zamorins, each leaving a significant cultural imprint. The arrival of Christianity, Islam, and Judaism in Kerala can be traced back to these ancient trading routes.
Historical Significance of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has played a pivotal role in India’s history. It is home to many of the country’s most important historical and religious sites, including Varanasi, Ayodhya, and Agra. The state was the epicenter of several major empires, including the Maurya, Gupta, and Mughal empires. UP also played a crucial role in India’s struggle for independence, with key figures like Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru being closely associated with the state.
Key Cultural Practices and Traditions
Kerala is known for its rich cultural heritage, which includes classical arts like Kathakali and Mohiniyattam, traditional music, and unique festivals such as Onam and Vishu. The state’s culture is a blend of Dravidian and Aryan influences, with significant contributions from the various communities that have lived there over the centuries.
Uttar Pradesh, with its deep-rooted traditions, is the heartland of many aspects of Indian culture. It is the birthplace of Hindi and Urdu literature and is known for its classical dance form Kathak, traditional music, and festivals like Diwali, Holi, and Eid. The state’s cultural diversity is reflected in its numerous religious and folk traditions.
Language and Ethnic Diversity
Malayalam is the official language of Kerala, and it is spoken by the majority of the population. The state is relatively homogenous in terms of ethnicity, with the Malayali people forming the largest ethnic group. However, Kerala also has significant communities of Tamils, Kannadigas, and Tuluvas.
Uttar Pradesh is linguistically and ethnically diverse. Hindi is the official language, but several dialects such as Awadhi, Bhojpuri, and Braj Bhasha are widely spoken. The state has a mix of various ethnic groups, including Brahmins, Yadavs, Thakurs, Dalits, and Muslims, contributing to its rich cultural mosaic.
Economic Overview
GDP and Economic Growth
Uttar Pradesh, despite its large population, has a lower GDP per capita compared to Kerala. The state’s economy is primarily driven by agriculture, manufacturing, and services. In recent years, there has been a push towards industrialization and urban development, with sectors like IT and tourism gaining traction.
Kerala, though smaller in size, has a higher GDP per capita, driven by a diverse economy that includes services, tourism, and remittances from the large number of Keralites working abroad. The state’s economic growth is supported by its high literacy rate, well-developed infrastructure, and emphasis on human development.
Key Industries in Kerala
The service sector is the backbone of Kerala’s economy, contributing significantly to its GDP. Tourism, healthcare, and education are major industries, along with traditional industries like coir, handloom, and spices. The state also benefits from remittances sent by the large expatriate community working in the Gulf countries.
Key Industries in Uttar Pradesh
Agriculture is the dominant sector in Uttar Pradesh, with the state being a leading producer of wheat, sugarcane, and rice. The state also has a growing manufacturing sector, particularly in textiles, leather goods, and handicrafts. The services sector, including IT and tourism, is expanding, especially in urban centers like Noida and Agra.
Employment Patterns and Unemployment Rates
Kerala has one of the highest unemployment rates in India, despite its high literacy rate. This paradox is largely due to the mismatch between the skills of the educated workforce and the available job opportunities within the state. Many Keralites seek employment abroad or in other parts of India.
Uttar Pradesh, with its large population, faces significant challenges in providing employment. The state has a high rate of underemployment, particularly in rural areas where agriculture is the primary source of livelihood. The government has launched several initiatives to promote skill development and job creation, particularly in the manufacturing and IT sectors.
Agriculture and Food Production
Agricultural Practices in Kerala
Agriculture in Kerala is characterized by small, fragmented landholdings and a focus on cash crops like rubber, tea, coffee, and spices. Rice is the staple food crop, but the state is not self-sufficient in food grains and relies on imports from other states. The agricultural sector in Kerala is facing challenges like declining productivity and increasing cost of cultivation.
Agricultural Practices in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh is known as the “granary of India” due to its significant contribution to the country’s food grain production. The state has a well-developed irrigation system, with rivers like the Ganges and Yamuna providing water for agriculture. Major crops include wheat, rice, sugarcane, and pulses. The state also has a significant dairy industry, contributing to its agricultural output.
Major Crops and Food Production
In Kerala, the major crops include rice, coconut, rubber, tea, coffee, and spices like black pepper and cardamom. The state’s tropical climate is ideal for the cultivation of these crops. Kerala is also a leading producer of rubber in India.
Uttar Pradesh is a major producer of wheat, sugarcane, rice, and pulses. The state’s fertile soil and well-developed irrigation infrastructure make it one of the most important agricultural states in India. Sugarcane is particularly significant, with UP being the largest producer of sugar in the country.
Contribution to National Food Security
Uttar Pradesh plays a crucial role in India’s food security, contributing a significant share of the country’s wheat and rice production. The state’s agricultural output is vital for feeding its large population as well as for export to other states.
Kerala, despite its high literacy rate and human development indicators, is not a major contributor to national food security in terms of grain production. The state focuses more on cash crops and relies on imports for staple food grains like rice and wheat.
Infrastructure and Development
Transportation Networks in Kerala
Kerala has a well-developed transportation network, with road, rail, and air connectivity covering most parts of the state. The state’s road density is one of the highest in India, and it has a significant number of national highways. The rail network connects major cities like Thiruvananthapuram, Kochi, and Kozhikode. Kerala also has three international airports, facilitating easy access to global destinations.
Transportation Networks in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has an extensive transportation network, with a vast network of roads, railways, and airports. The state has several national highways and expressways, including the Yamuna Expressway and the Agra-Lucknow Expressway, which are crucial for connectivity. The rail network is extensive, with major railway junctions like Kanpur and Varanasi serving as important hubs. UP also has several airports, including international ones in Lucknow and Varanasi.
Urban Development and Smart Cities
Kerala has made significant strides in urban development, with cities like Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram being developed as smart cities. These cities are focusing on improving infrastructure, promoting sustainable development, and enhancing the quality of life for residents. The state government is also promoting the development of satellite towns to decongest major urban centers.
Uttar Pradesh is focusing on urban development through initiatives like the Smart Cities Mission, with cities like Kanpur, Lucknow, and Varanasi being selected for development. The state is working on improving infrastructure, enhancing public services, and promoting sustainable urban growth. The development of new townships and industrial corridors is also a key focus area.
Rural Development Initiatives
Kerala has a strong tradition of rural development, with programs focused on improving healthcare, education, and infrastructure in rural areas. The state’s decentralized governance model, with a focus on local self-government, has been successful in promoting rural development.
Uttar Pradesh has several rural development initiatives aimed at improving the quality of life in villages. Programs like the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) and the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) are being implemented to provide housing, employment, and basic amenities to the rural population.
Education and Literacy
Education System in Kerala
Kerala’s education system is one of the most developed in India, with a strong emphasis on universal primary education and high literacy rates. The state has a well-established network of schools and colleges, with a focus on quality education. Kerala also has a significant number of higher education institutions, including universities, medical colleges, and engineering colleges.
Education System in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh’s education system, while improving, faces challenges like inadequate infrastructure, high dropout rates, and disparities in access to education between urban and rural areas. The state government has launched several initiatives to improve the quality of education, including the construction of new schools, teacher training programs, and scholarships for students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Higher Education and Research Institutions
Kerala has a number of prestigious higher education institutions, including the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Palakkad, the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Thiruvananthapuram, and several medical and engineering colleges. The state is also known for its research institutions, particularly in the fields of science and technology.
Uttar Pradesh is home to several renowned universities and research institutions, including the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur, Banaras Hindu University (BHU), and the Aligarh Muslim University (AMU). These institutions are known for their contributions to education and research, particularly in the fields of engineering, science, and the humanities.
Government Initiatives and Schemes
Kerala’s government has implemented various initiatives to promote education, including the midday meal scheme, scholarships for students from disadvantaged backgrounds, and programs to promote digital literacy. The state’s focus on education has been instrumental in achieving high literacy rates and educational outcomes.
The government of Uttar Pradesh has launched several initiatives to improve education, including the construction of new schools, teacher training programs, and scholarships for students from disadvantaged backgrounds. The state is also focusing on improving the quality of education in rural areas, where access to education has historically been limited.
Healthcare System
Overview of Healthcare in Kerala
Kerala is widely recognized for its well-developed healthcare system, which is considered one of the best in India. The state has a robust public healthcare network, with a large number of government hospitals, primary health centers, and community health centers. Kerala also has a thriving private healthcare sector, with several renowned hospitals and medical institutions. The state’s focus on preventive healthcare and public health initiatives has resulted in high life expectancy, low infant mortality, and a strong overall health profile.
Overview of Healthcare in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh faces significant challenges in providing healthcare to its large population. The state has a high infant mortality rate and a low life expectancy compared to the national average. The public healthcare system is underfunded and understaffed, particularly in rural areas. However, the state government is making efforts to improve healthcare services through initiatives like the National Health Mission (NHM) and the Ayushman Bharat scheme, which aims to provide affordable healthcare to low-income families.
Health Indicators (Infant Mortality, Life Expectancy)
Kerala has some of the best health indicators in India, with an infant mortality rate of around 6 per 1,000 live births and a life expectancy of about 75 years. These achievements are largely due to the state’s focus on healthcare, education, and social development.
In contrast, Uttar Pradesh has one of the highest infant mortality rates in India, at around 43 per 1,000 live births, and a life expectancy of about 65 years. The state’s healthcare challenges are compounded by its large population, poverty, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure.
Public Health Initiatives and Challenges
Kerala’s public health initiatives, including immunization programs, maternal and child health services, and disease prevention campaigns, have been successful in improving health outcomes. However, the state faces challenges like the increasing burden of non-communicable diseases and the need to improve healthcare access in remote areas.
Uttar Pradesh’s public health initiatives focus on addressing key challenges like maternal and child health, infectious diseases, and malnutrition. The state has launched several programs to improve healthcare access, particularly in rural areas. However, the large population and widespread poverty present significant challenges in achieving better health outcomes.
Political Landscape
Governance Structure in Kerala
Kerala has a well-established governance structure, with a strong tradition of coalition politics. The state has a unicameral legislature, with a legislative assembly and a governor. The state’s political landscape is dominated by two major coalitions: the Left Democratic Front (LDF) and the United Democratic Front (UDF). The state is known for its progressive policies, particularly in the areas of education, healthcare, and social welfare.
Governance Structure in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has a bicameral legislature, with a legislative assembly and a legislative council. The state is governed by a chief minister and a council of ministers, with the governor serving as the ceremonial head of state. UP’s political landscape is highly competitive, with several major political parties, including the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), the Samajwadi Party (SP), and the Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP), vying for power. The state has a history of caste-based politics and is often seen as a bellwether for national elections.
Political History and Key Figures
Kerala’s political history is marked by the dominance of left-wing politics, with the Communist Party of India (Marxist) playing a significant role in the state’s governance. The state has produced several prominent political figures, including E.M.S. Namboodiripad, the first chief minister of Kerala and a key figure in India’s communist movement.
Uttar Pradesh has a rich political history, being the home state of several prominent Indian leaders, including Jawaharlal Nehru, India’s first prime minister, and Indira Gandhi, the country’s first female prime minister. The state has also been a stronghold for the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) in recent years, with Yogi Adityanath serving as the current chief minister.
Current Political Dynamics
In Kerala, the political dynamics are shaped by the rivalry between the Left Democratic Front (LDF) and the United Democratic Front (UDF). The state’s electorate is known for its political awareness and high voter turnout, with elections often resulting in a change of power between the two coalitions.
In Uttar Pradesh, the political dynamics are dominated by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), which has been in power since 2017. The state’s politics are characterized by caste-based voting patterns, with major parties like the Samajwadi Party (SP) and the Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) drawing support from specific caste groups. The BJP’s focus on Hindutva and development has resonated with a broad section of the electorate.
Tourism and Travel
Major Tourist Attractions in Kerala
Kerala is a popular tourist destination, known for its natural beauty, backwaters, and cultural heritage. Major tourist attractions include the hill stations of Munnar and Wayanad, the beaches of Kovalam and Varkala, the backwaters of Alleppey, and the historic city of Kochi. Kerala is also known for its wellness tourism, with a focus on Ayurveda and holistic healing.
Major Tourist Attractions in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh is home to some of India’s most iconic tourist destinations, including the Taj Mahal in Agra, the holy city of Varanasi, and the ancient city of Ayodhya. The state is also known for its religious tourism, with millions of pilgrims visiting sites like Mathura, Vrindavan, and Prayagraj (Allahabad) each year. UP’s rich history and cultural heritage make it a must-visit destination for tourists.
Impact of Tourism on Local Economies
Tourism is a major contributor to Kerala’s economy, providing employment to a significant portion of the population. The state has successfully leveraged its natural and cultural assets to attract both domestic and international tourists. The revenue generated from tourism supports various sectors, including hospitality, transport, and handicrafts.
In Uttar Pradesh, tourism plays a crucial role in the state’s economy, particularly in cities like Agra and Varanasi. The state’s focus on religious and cultural tourism has helped boost local economies, providing livelihoods to millions of people. However, there is still potential for growth in areas like infrastructure development and sustainable tourism practices.
Challenges in Promoting Tourism
Kerala faces challenges in promoting tourism, including the need to improve infrastructure, manage environmental sustainability, and diversify its tourism offerings. The state is working to address these challenges through initiatives like responsible tourism and the development of new tourist circuits.
Uttar Pradesh’s challenges in promoting tourism include inadequate infrastructure, overcrowding at major tourist sites, and the need to improve safety and security for tourists. The state government is taking steps to address these issues, including the development of new tourism infrastructure and the promotion of lesser-known destinations.
Social Issues and Challenges
Poverty and Inequality in Kerala
Kerala has made significant progress in reducing poverty and inequality, thanks to its focus on social welfare, education, and healthcare. The state has one of the lowest poverty rates in India and is known for its relatively equitable distribution of wealth. However, challenges remain, particularly in addressing regional disparities and ensuring economic opportunities for all.
Poverty and Inequality in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh faces significant challenges in addressing poverty and inequality. The state has one of the highest poverty rates in India, with a large portion of the population living below the poverty line. Inequality is also a major issue, with stark disparities in income, education, and access to basic services between urban and rural areas.
Gender Equality and Women’s Empowerment
Kerala is often cited as a model for gender equality and women’s empowerment in India. The state has a high female literacy rate, low gender disparity in education, and a strong presence of women in the workforce. Kerala’s social indicators for women, such as maternal mortality and female life expectancy, are among the best in the country.
Uttar Pradesh, on the other hand, faces significant challenges in achieving gender equality. The state has a low female literacy rate, high levels of gender-based violence, and limited economic opportunities for women. The state government has launched various initiatives to promote women’s empowerment, including schemes for girl child education and women’s health.
Crime Rates and Law Enforcement
Kerala has a relatively low crime rate compared to other Indian states, with a strong focus on law enforcement and community policing. The state’s police force is known for its efficiency and public trust, and Kerala’s legal system is relatively accessible to the general population.
Uttar Pradesh has one of the highest crime rates in India, with significant challenges in law enforcement and public safety. The state’s police force is often criticized for inefficiency, corruption, and a lack of accountability. However, the state government is working to improve law enforcement through reforms, modernization, and community engagement.
Environmental Concerns
Environmental Challenges in Kerala
Kerala faces several environmental challenges, including deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and pollution of rivers and backwaters. The state is also vulnerable to natural disasters like floods and landslides, which have become more frequent in recent years due to climate change. Kerala’s government is focusing on sustainable development and conservation efforts to address these challenges.
Environmental Challenges in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh faces significant environmental challenges, including air and water pollution, deforestation, and soil degradation. The state’s industrial activities and high population density contribute to environmental degradation, particularly in urban areas. UP is also vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, with rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns affecting agriculture and water resources.
Conservation Efforts and Policies
Kerala has implemented several conservation initiatives, including the protection of forests and wildlife, promotion of sustainable tourism, and management of natural resources. The state’s efforts to conserve the Western Ghats, a biodiversity hotspot, have been recognized globally.
Uttar Pradesh has launched various conservation efforts, including afforestation programs, pollution control measures, and the protection of wildlife habitats. The state government is also focusing on sustainable development practices and the promotion of renewable energy to reduce its environmental footprint.
Impact of Climate Change
Kerala is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, with rising sea levels, changing rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of natural disasters posing significant risks. The state is working on climate adaptation strategies, including disaster preparedness, coastal zone management, and the promotion of climate-resilient agriculture.
Uttar Pradesh is also affected by climate change, with rising temperatures, erratic rainfall, and increased frequency of droughts and floods impacting agriculture and water resources. The state government is focusing on climate adaptation and mitigation strategies, including the promotion of water conservation, renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture practices.
Comparative Analysis
Key Strengths of Kerala
Kerala’s key strengths lie in its high literacy rate, well-developed healthcare system, and strong social indicators. The state’s emphasis on education, healthcare, and social welfare has resulted in a high Human Development Index (HDI) and a relatively high standard of living. Kerala’s natural beauty and cultural heritage also make it a popular tourist destination, contributing to its economy.
Key Strengths of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh’s strengths include its large agricultural output, rich cultural heritage, and strategic location in northern India. The state’s economy is driven by agriculture, manufacturing, and services, with significant potential for growth in sectors like IT and tourism. UP’s historical and religious significance also makes it a key destination for tourists and pilgrims.
Areas of Improvement for Both States
Kerala needs to focus on addressing its high unemployment rate, improving infrastructure, and promoting economic diversification to reduce its reliance on remittances. The state also needs to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable development practices.
Uttar Pradesh faces significant challenges in improving education and healthcare, reducing poverty and inequality, and addressing environmental degradation. The state also needs to focus on improving law enforcement, infrastructure, and governance to promote sustainable development and improve the quality of life for its residents.
Recent Developments in Kerala
1. Digital University of Kerala:
Kerala has launched the Digital University of Kerala, the first of its kind in the state, focusing on digital technologies and innovation. This initiative is part of Kerala’s larger push towards becoming a hub for technology and digital education, aiming to create a skilled workforce for the future.
2. SilverLine Semi-High-Speed Rail Project:
The Kerala government has proposed the SilverLine project, a semi-high-speed rail corridor that will connect the northern and southern parts of the state. This ambitious project aims to reduce travel time across the state significantly and boost economic growth by improving connectivity.
3. Covid-19 Vaccination and Health Initiatives:
Kerala has been at the forefront of Covid-19 vaccination efforts in India, achieving high vaccination coverage. The state has also strengthened its healthcare infrastructure, including setting up new oxygen plants and increasing ICU capacity in response to the pandemic.
4. Kerala Knowledge Economy Mission:
Launched by the Kerala government, this mission aims to provide employment to 20 lakh educated youths by focusing on knowledge-based industries. The initiative is designed to harness Kerala’s high literacy rate and create job opportunities in sectors like IT, biotechnology, and finance.
Recent Developments in Uttar Pradesh
1. UP Defense Corridor:
Uttar Pradesh is developing a Defense Industrial Corridor aimed at boosting the state’s manufacturing sector and making it a hub for defense production. This initiative is expected to attract investments, create jobs, and strengthen the state’s industrial base.
2. Jewar International Airport:
Construction of the Jewar International Airport near Noida is underway, which will be the largest airport in India upon completion. This project is expected to enhance air connectivity, boost tourism, and spur economic growth in the region.
3. Kashi Vishwanath Corridor Project:
The Kashi Vishwanath Corridor in Varanasi is a major redevelopment project aimed at improving the infrastructure around the historic Kashi Vishwanath Temple. The project includes new amenities for pilgrims and tourists, making the area more accessible and enhancing the spiritual tourism experience.
4. Mission Shakti for Women’s Empowerment:
The Uttar Pradesh government has launched Mission Shakti, an extensive program focusing on women’s safety, security, and empowerment. The initiative includes setting up women help desks, enhancing legal aid for women, and promoting women-led enterprises.
These developments highlight the ongoing efforts in both states to improve infrastructure, boost economic growth, and address social issues, reflecting their dynamic and evolving nature.
Future Prospects and Development Pathways
Kerala’s future prospects lie in its ability to leverage its strengths in education, healthcare, and tourism to promote sustainable development. The state is focusing on promoting innovation, improving infrastructure, and addressing environmental challenges to ensure long-term growth and development.
Uttar Pradesh’s future development will depend on its ability to address key challenges in education, healthcare, and governance. The state is focusing on promoting industrialization, improving infrastructure, and enhancing public services to ensure sustainable economic growth and improve the quality of life for its residents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Kerala and Uttar Pradesh are two diverse and dynamic states that represent different aspects of India’s cultural, economic, and geographical landscape. While Kerala is known for its high literacy rate, well-developed healthcare system, and natural beauty, Uttar Pradesh is recognized for its large population, rich cultural heritage, and significant agricultural output. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two states provides valuable insights into the diversity and complexity of India as a whole.
FAQs
1. What are the major economic differences between Kerala and Uttar Pradesh?
Kerala has a higher GDP per capita and is driven by the service sector, tourism, and remittances, while Uttar Pradesh’s economy is primarily driven by agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
2. How does the education system in Kerala compare to Uttar Pradesh?
Kerala has a higher literacy rate and a well-developed education system with a focus on quality education, while Uttar Pradesh faces challenges like inadequate infrastructure and high dropout rates.
3. What are the key cultural differences between Kerala and Uttar Pradesh?
Kerala is known for its classical arts, festivals, and unique cultural practices, while Uttar Pradesh is the heartland of Hindi and Urdu literature, with a rich tradition of classical dance, music, and religious festivals.
4. How do healthcare facilities differ between Kerala and Uttar Pradesh?
Kerala has a well-developed healthcare system with high health indicators, while Uttar Pradesh faces challenges in providing adequate healthcare services, particularly in rural areas.
5. Which state has a better quality of life, Kerala or Uttar Pradesh?
Kerala generally has a higher quality of life, with better social indicators like literacy, life expectancy, and healthcare, while Uttar Pradesh faces challenges in these areas due to its large population and economic disparities.