Introduction
In the colorful world of cartoons, characters come in all shapes and sizes. Among these, fat cartoon characters often stand out, not just for their physical appearance but for the unique and memorable personalities they bring to the screen. In a society where media representation significantly influences public perception, the depiction of diverse body types in cartoons can play a crucial role in promoting positivity and inclusivity. This article explores the world of fat cartoon characters, their impact on viewers, and how we can remain positive and appreciative of body diversity in media.
Historical Context of Fat Cartoon Characters
The evolution of cartoon characters’ body types reflects broader societal attitudes towards body diversity. In the early days of animation, characters were often drawn with exaggerated features to emphasize their personalities. Fat characters frequently played the roles of villains, buffoons, or comic relief, reinforcing negative stereotypes about weight.
One of the earliest examples of a fat cartoon character is Bluto from the Popeye series. Bluto’s large, muscular frame and antagonistic role exemplified the era’s tendency to link physical size with negative traits. However, as society began to challenge these stereotypes, the representation of fat characters started to shift.
Popular Fat Cartoon Characters
Several fat cartoon characters have become beloved icons, celebrated for their distinctive traits and the joy they bring to audiences. Here are a few notable examples:
1. Homer Simpson (The Simpsons):
Homer, the bumbling yet lovable father figure, embodies the everyman. Despite his numerous flaws, his character is portrayed with warmth and humor, making him relatable to many viewers.
2. Peter Griffin (Family Guy):

Similar to Homer, Peter Griffin is characterized by his humorous escapades and endearing ignorance. His size is a part of his character but does not define his entire persona.
3. Pumbaa (The Lion King):

As a friendly warthog with a heart of gold, Pumbaa teaches valuable lessons about friendship and self-acceptance. His character challenges the notion that size determines worth.
4. Ursula (The Little Mermaid):

Although a villain, Ursula’s confidence and charisma make her a standout character. Her portrayal has sparked discussions about body image and the complexity of villainy in media.
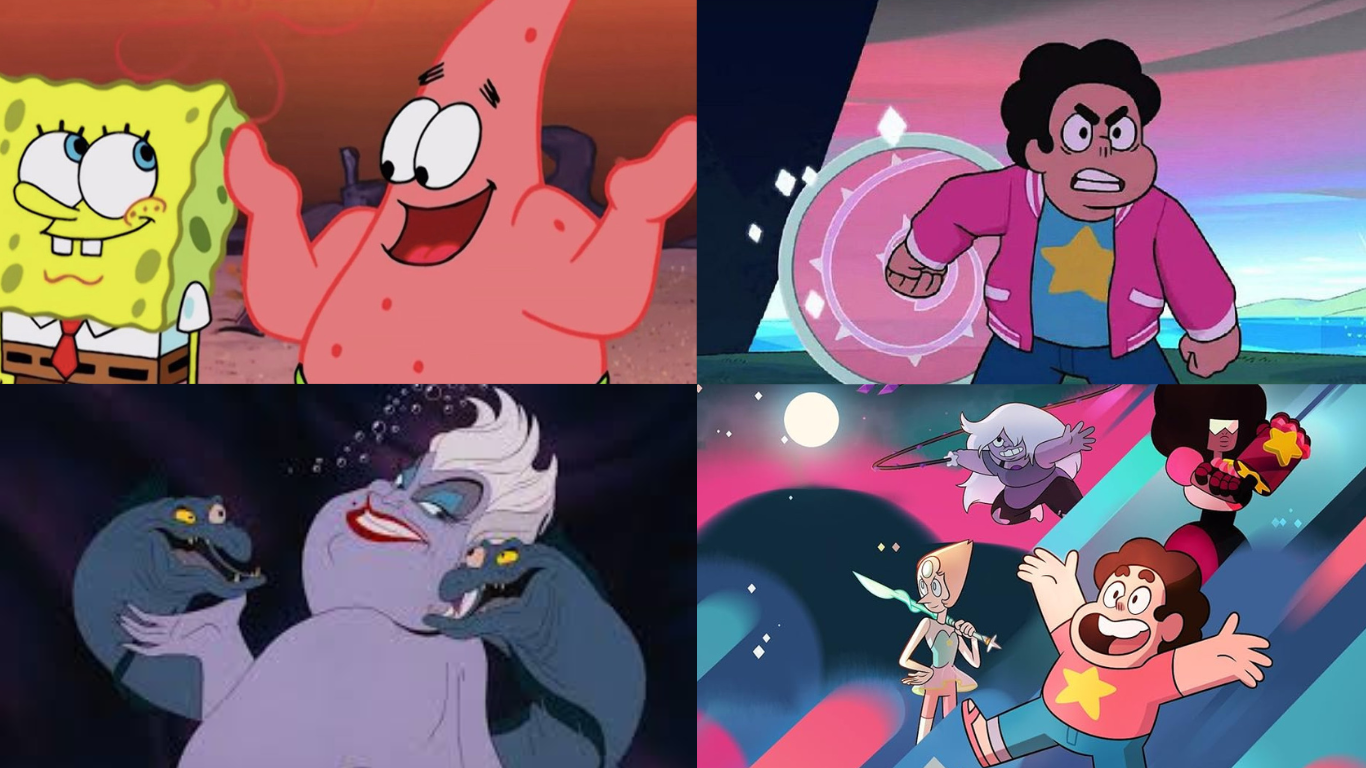
5. Patrick Star (SpongeBob SquarePants):

Patrick’s laid-back attitude and simple-mindedness make him a source of comic relief. His friendship with SpongeBob highlights the importance of loyalty and acceptance.
Representation and Its Impact
Positive representation in media can significantly influence audience perceptions and self-image. Fat cartoon characters, when depicted with depth and nuance, contribute to a more inclusive media landscape. These characters show that being fat is just one aspect of a multifaceted identity, helping to dismantle harmful stereotypes.
Research has shown that diverse media representation can improve self-esteem and reduce the stigma associated with different body types. For instance, seeing a character like Homer Simpson who is accepted and loved by his family despite his imperfections can provide reassurance and foster a sense of belonging among viewers.
Body Positivity in Media
Body positivity is a movement that encourages acceptance and appreciation of all body types. In the context of cartoons, promoting body positivity involves creating characters that reflect the diversity of human bodies and presenting them in empowering ways.
Several cartoons have made strides in this area by featuring fat characters who are strong, capable, and central to the storyline. For example, Steven Universe from the show of the same name is a chubby boy who is also a hero. His character breaks traditional stereotypes by combining physical diversity with positive traits like bravery, kindness, and intelligence.
Common Stereotypes and Misrepresentations
Despite progress, fat characters in cartoons are still sometimes portrayed through a lens of stereotypes. Common tropes include the “jolly fat person,” the “glutton,” and the “lazy individual.” These representations can reinforce negative perceptions and contribute to the stigmatization of fat bodies.
One example is Fat Albert, a character created by Bill Cosby in the 1970s. While Fat Albert was depicted as kind-hearted and a leader among his friends, the show’s emphasis on his weight often reinforced the stereotype of the “lovable fat guy.” Although the character had positive traits, the constant focus on his size could overshadow his other qualities.
Breaking Stereotypes: Modern Examples
Fortunately, modern cartoons are increasingly challenging these outdated stereotypes by presenting fat characters in more complex and positive ways. Here are a few examples:
1. Pearl Krabs (SpongeBob SquarePants):

Pearl is Mr. Krabs’ teenage daughter, a whale with a vibrant personality and diverse interests. Her size is never the focus of her character, allowing her other traits to shine through.
2. Baymax (Big Hero 6):

Baymax is a robot designed to provide healthcare, and his large, inflatable body is integral to his function. His gentle nature and dedication to helping others make him a beloved character, showing that size and shape can be assets rather than limitations.
3. Steven Universe (Steven Universe):
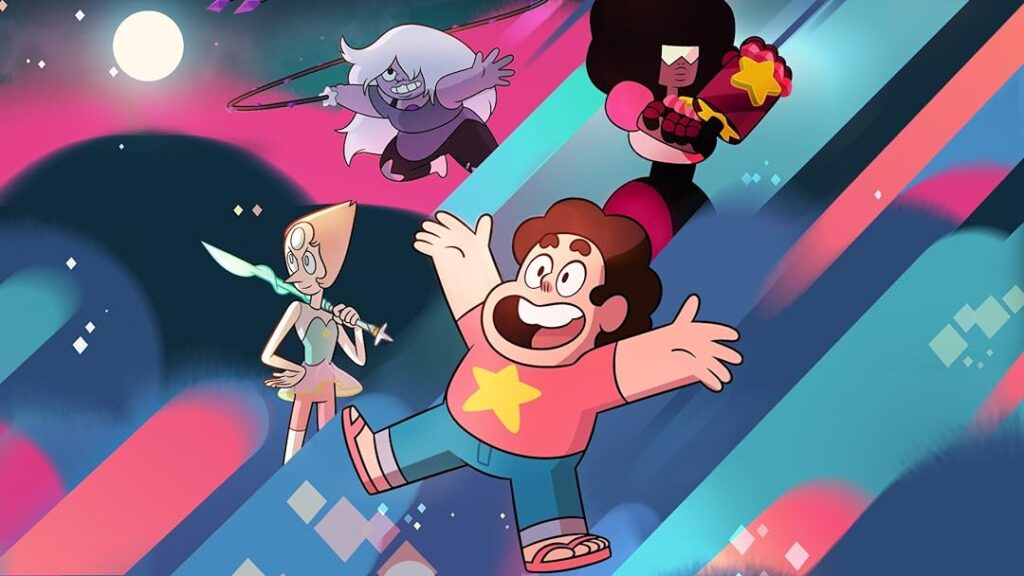

Steven’s character is groundbreaking in many ways. His chubby physique is portrayed positively, and his emotional intelligence, bravery, and compassion make him a well-rounded and inspirational hero.
These characters demonstrate that fat bodies can be associated with strength, intelligence, kindness, and other positive attributes, helping to shift public perception.
How to Remain Positive While Consuming Media
In a media landscape that often emphasizes unrealistic body standards, it’s important to adopt a critical approach to media consumption. Here are some tips for maintaining a positive mindset:
- Be Critical of Stereotypes: Recognize and question stereotypes when they appear. Understanding the harmful effects of these portrayals can help you avoid internalizing negative messages.
- Seek Out Diverse Representation: Support and consume media that features a wide range of body types and positive portrayals of fat characters. This helps to reinforce the idea that all bodies are valuable.
- Practice Self-Love: Engage in activities that promote self-acceptance and appreciation of your own body. Surround yourself with positive influences, both online and offline.
- Engage in Positive Conversations: Discuss body diversity and media representation with friends and family. Sharing perspectives can foster a more inclusive environment and help combat negative stereotypes.
The Role of Content Creators
Content creators hold significant power in shaping public perceptions through the characters and stories they produce. By prioritizing diversity and inclusivity, they can contribute to a more positive media landscape.
Several initiatives and movements are encouraging creators to develop more inclusive content. For example, the Body Positive Movement advocates for the representation of all body types in media, pushing for characters that reflect the real-world diversity of human bodies.
Creators can also engage with audiences to understand their perspectives and needs. By listening to feedback and incorporating diverse voices into the creative process, they can produce content that resonates with a broader audience and promotes positive messages about body image.
Community and Support
Building a supportive community around body positivity can help individuals feel more confident and accepted. There are numerous online forums, social media groups, and organizations dedicated to promoting body positivity and inclusivity in media.
For example, the Body Positive Alliance provides resources and support for individuals seeking to promote body diversity in their communities. By joining such groups, individuals can find like-minded people, share experiences, and access valuable resources.
Additionally, following influencers and activists who advocate for body positivity can provide daily inspiration and motivation. Figures like Tess Holliday, a plus-size model and activist, use their platforms to challenge beauty standards and promote self-acceptance.
Conclusion
Fat cartoon characters play a vital role in promoting diversity and inclusivity in media. By celebrating these characters and challenging negative stereotypes, we can foster a more positive and accepting society. As viewers, it is important to remain critical of media portrayals, support diverse representation, and practice self-love.
By encouraging content creators to prioritize inclusivity and engaging with supportive communities, we can continue to push for positive change. Let’s celebrate the richness of human diversity and appreciate the unique contributions that fat cartoon characters bring to our screens.
Additional Resources
For those interested in further exploring body positivity and representation in media, here are some recommended resources:
- Books: “Body Positive Power” by Megan Jayne Crabbe, “The Body Is Not an Apology” by Sonya Renee Taylor
- Documentaries: “Embrace” directed by Taryn Brumfitt, “Fat Fiction” directed by Jennifer Isenhart
- Cartoons: “Steven Universe,” “Big Hero 6,” “Adventure Time”
FAQs
Q1: Why is representation of fat cartoon characters important?
A: Representation of fat cartoon characters is crucial because it promotes body diversity, challenges negative stereotypes, and helps viewers feel accepted and valued regardless of their body size.
Q2: Which are some popular fat cartoon characters?
A: Some popular fat cartoon characters include Homer Simpson from “The Simpsons,” Peter Griffin from “Family Guy,” Pumbaa from “The Lion King,” Ursula from “The Little Mermaid,” and Patrick Star from “SpongeBob SquarePants.”
Q3: How do fat cartoon characters impact viewers’ perceptions?
A: Fat cartoon characters can positively impact viewers by providing relatable and diverse representations, improving self-esteem, and reducing the stigma associated with different body types.
Q4: What are some common stereotypes about fat cartoon characters?
A: Common stereotypes about fat cartoon characters include being portrayed as lazy, gluttonous, or solely as comic relief. These stereotypes can reinforce negative perceptions about weight.
Q5: How can content creators promote positive representation of fat characters?
A: Content creators can promote positive representation by developing well-rounded, diverse characters, avoiding stereotypes, and engaging with audiences to understand their perspectives on body diversity.
Q6: What are some modern examples of cartoons that break stereotypes about fat characters?
A: Modern examples include Pearl Krabs from “SpongeBob SquarePants,” Baymax from “Big Hero 6,” and Steven Universe from “Steven Universe,” who are depicted with positive traits and complex personalities.
Q7: How can individuals remain positive while consuming media?
A: Individuals can remain positive by critically analyzing media portrayals, seeking out diverse representations, practicing self-love, and engaging in conversations about body positivity.
Q8: Are there any resources for learning more about body positivity in media?
A: Yes, recommended resources include books like “Body Positive Power” by Megan Jayne Crabbe, articles from The Representation Project, documentaries like “Embrace,” and online communities such as the Body Positive Alliance.




